With the Shanghai upgrade for Ethereum set to take place in April, the ability to withdraw staked ETH will also become available. As the upgrade approaches, interest in liquid staking protocols has risen, with many community members wanting to know how the industry will adapt.
In this guide, we’ll cover the mechanics behind liquid staking, significant liquid staking operations, the trade-offs between liquid staking, solo staking, and staking-as-a-service, the role liquid staking will play for the future of Ethereum, and how to boost your staking rewards.
The Complexity of Staking
Generally, staking represents locking a blockchain’s native token as a way of participating in the network’s consensus process. In a conventional staking process tokens are completely locked and it is impossible to utilize the staked assets for any other activity in parallel.
This is the default staking process on Ethereum. As a solo-staker, running an Ethereum validator entails meeting certain hardware and software requirements for operating a validator node, as well as a minimum stake of 32 ETH. This process necessitates a certain level of technical expertise.
There is also a similar option available known as staking-as-a-service for users that have 32 ETH but do not feel comfortable with the technical aspects of operating their own node. This allows them to deposit 32 ETH with an existing node operator that will run the necessary software for a fee based on the staking rewards.
Because many members of the Ethereum community do not possess the technical proficiency, time, and/or financial resources necessary for operating a validator node, an alternative option is available through the utilization of liquid staking protocols.
How Liquid Staking Makes Staking Accessible
Liquid staking is an option that is useful for users that do not have 32 ETH, or who have a sufficient amount of ETH but do not feel comfortable with operating their own validator or utilizing a staking-as-a-service provider. Liquid staking allows like-minded members of the Ethereum ecosystem to instead pool their coins together in a manner that allows dedicated liquid staking pool solutions to manage validator nodes on their behalf.
When you participate in pooled liquid staking, you generally exchange your ETH for a receipt liquid staking token distributed by the staking pool. This liquid staking token represents the ETH you have staked in the pool and becomes your key to redeeming your original funds and tracking cumulative staking rewards that the pool assigns to you.
Protocols differ in exactly how they distribute rewards, but this general flow is what you can expect when interacting with a liquid staking solution. At the moment, liquid staking represents 33% of all staking on the Ethereum network.
Note: In the past, liquid staking tokens have sometimes been referred to as "liquid staking derivatives" or "LSDs", but this is not technically correct.
The Benefits of Liquid Staking
Convenience
There is no faster way to begin participating in staking Ethereum than utilizing a liquid staking pool. Most liquid staking protocols are as easy to join as completing a Uniswap transaction. And while staking via centralized exchanges is generally convenient as well, it can be a headache for users that do not already have an exchange account. Liquid staking, by comparison, requires no traditional sign-up process. The only things a user requires are ETH, a web3 wallet, and an internet connection.
Cost Effectiveness
While the Ethereum ecosystem benefits from having a diverse set of validators with 32 ETH deposited to run nodes, the reality is that 32 ETH is a significant sum of money for most participants in the ecosystem. Liquid staking allows smaller users to still have their voice heard in the act of on-chain security and governance by deciding which liquid staking providers they want to utilize.
Liquidity
The primary benefit of liquid staking is that, while other forms of staking force you to completely lock your coins and their associated capital, it instead allows you to participate in providing security via staking while still having access to some form of capital. Liquid staking tokens are tradable and therefore offer far more flexibility in accessing capital as opposed to directly staking as an individual Ethereum validator.
If a solo staking validator wishes to access their capital, they must wait in an algorithmic queue based on the amount they need to withdraw from the network. While some users do not mind this delay, others prefer to have access to capital when needed. This dynamic also means that the network can expect a continued demand for liquid staking even after withdrawals are enabled by Shanghai.
Smoothed Rewards
One of the unique characteristics of pooled staking is that your rewards are “smoothed” when compared to an individual Ethereum validator. While individual validators may vastly outperform (or underperform) average staking rewards based on the potential to capture exceptionally valuable block rewards, this will not be the case for users that participate in pools. The pool itself will likely win blocks that are more valuable than average, but it will be balanced by lower-value blocks as well. Pool operators will then even out these fluctuations in value when distributing rewards to all members.
The Drawbacks of Liquid Staking
Pool Operator Fees
There is a price paid for the convenience afforded by liquid staking. All liquid staking pool solutions take a margin of the staking rewards that they manage as a form of compensation for their services. On average this commission ranges from 10% - 20% of the ETH rewards that a staker would otherwise receive.
Network Centralization
The goal of any robust cryptocurrency staking system should be to have a decentralized network that is resistant to centralized failure points. The nature of liquid staking, where a central provider can manage funds for outside users, creates friction with this overall goal.
Lido has outlined in their blog that, “The staking landscape may be more centralized than the mining landscape, supporting fewer, more concentrated winners…a staking pool’s ability to issue liquid staking tokens like stETH creates a powerful network effect”. To address this issue, all liquid staking providers take steps to decentralize their platform to varying degrees. We will outline some of the strategies in place within our Liquid Staking Options overview.
Pool Operator Failure
While users that participate in liquid staking platforms receive receipts in the form of the operator's liquid staking token, these tokens are not fundamentally tied to the value of the ETH they are meant to represent. Should the individual pool operators mismanage users’ funds, holders of liquid staking tokens could find themselves in a situation where their assets are no longer backed by corresponding ETH.
Pool operator failure is by far the greatest risk to the health of the liquid staking ecosystem. Therefore, protocols place the utmost importance on the design of their systems to attract reputable individuals with systems in place to prevent the catastrophic loss of user funds due to slashing or improper validator key management.
One dramatic example of pool operator failure is StakeHound. StakeHound was a liquid staking operator that held over 38,000 ETH. Due to mismanagement of the corresponding cryptographic keys for their validators, they no longer can withdraw funds from the Beacon Chain and users have received no compensation.
The Correlation Penalty
The rules for calculating Ethereum’s slashing fees have a calculation multiplier in place to discourage collusion between dishonest validators. This is known as the “correlation penalty”. This penalty reflects the number of other validators slashed over the same time period. The maximum applicable amount can be as high as the total effective balance of the offender(s).
In the situation where a pool operator fails in their duties and incurs slashing penalties, they are at an elevated risk of triggering maximum penalties because it is likely that they will have multiple validators being slashed at once.
In such a situation, depositors will be at the whims of the pool operator to reimburse them, because there’s a potential for the maximum penalty to be as high as the offender’s entire balance. This exact scenario played out in February of 2021 when the staking pool Staked triggered a slashing penalty and had to repay users independently.
Liquid Staking Options for Stakers
For members of the Ethereum community that are interested in liquid staking, there are a variety of reputable options to choose from. We will outline some of the established players as well as provide information on up-and-coming liquid staking projects that have the potential to grow.
As always, the information provided here is intended for informational purposes only. APR information provided within is sourced directly from each staking solution site and may be subject to different calculation methods. Nothing in this document is investment, legal, or tax advice. Do your own research. Stay SAFU.
Lido
URL: https://lido.fi/
Liquid Staking Token: stETH
Lido is not only the largest liquid staking operation on Ethereum, they are the network's largest staking operation of all. Their website states that Lido “attempts to solve the problems associated with initial ETH staking - illiquidity, immovability and accessibility - making staked ETH liquid and allowing for participation with any amount of ETH to improve performance of the Ethereum network.”
The protocol was one of the first movers in liquid staking, publishing their first outline document in October 2020 and launching in December 2020 alongside Ethereum’s Beacon Chain. Lido’s open-source smart contracts perform the conversion of ETH to stETH. They also offer a suite of software protocols on multiple blockchains beyond Ethereum.
Lido Stats
- Total ETH Staked: 5,550,000 (source)
- Current APR: 6.6% (source)
- Percentage of Total Network: 31% (source)
- Unique Node Operators: 29 (source)
- Staking Commission Percentage: 10% (source)
- Self-Limited: The Lido DAO has voted against self-limiting
Governance Structure
Lido's software allocates ETH deposits across a varity of independent node operators based on a deterministic on-chain algorithm. Oversight of these operators is the responsibility of the Lido DAO. Voting rights in the DAO are controlled by the governance token LDO. Lido is pushing for the decentralization of their governance efforts. Their decentralization scorecard monitors progress towards this goal and governance discussions take place on their research forum.
How Payouts Work
Lido’s liquid token, stETH, uses a rebasing design. This means that the balance you hold of the token will continue to rise. Crucially, this process is automatic so there is no need for stakers to utilize ETH gas when claiming their rewards.
Below you can see how the balance of stETH held in a Metamask wallet will change over time.
Day 1 of staking

Day 5 of staking

How to Stake on Lido
Plans for Withdrawals
Lido has outlined their plans for processing withdrawals in this post. The flow will involve three steps:
- Request: To withdraw stETH to Ether, the user sends the withdrawal request to the WithdrawalQueue contract, locking the stETH amount to be withdrawn.
- Fulfillment: The protocol handles the requests one-by-one, in the order of creation. Once the protocol has enough information to calculate the stETH share redemption rate of the next request and obtains enough Ether to handle it, the request can be finalized: the required amount of Ether is reserved and the locked stETH is burned.
- Claim: The user can then claim their Ether at any time in the future. The stETH share redemption rate for each request is determined at the time of its finalization and is the inverse of the Ether/stETH staking rate.
The current estimate is that exchanges of stETH for ETH via the official withdrawal mechanism should take roughly 24-48 hours. Lido withdrawals are also part of an overall revamp of Lido known as Lido V2 which will encompass withdrawals and new validator capabilities.
Rocket Pool
Liquid Staking Token: rETH
Rocket Pool is a liquid staking pool that aims to lower the capital and hardware requirements for staking, thereby enhancing the decentralization and security of the Ethereum network. The protocol was originally designed in 2016 and Vitalik has been a fan since at least 2018.
Rocket Pool has by far the most unique node operators of any liquid staking protocol. By doing so, they counteract some of the centralizing forces that are a common critique of liquid staking.
Rocket Pool caters to two main user groups: those who wish to participate in tokenized staking using rETH (which continuously accrues value vs ETH), with as little as 0.01 ETH, and those who wish to stake ETH and operate a node in the network to generate a higher return on investment than staking outside of the protocol, due to earned commissions.
For detailed information on these two groups that make up the protocol, we highly recommend reading the first article in their explainer series which provides an in-depth look at how users can participate, whether through tokenized staking or operating a node in the protocol. The conversion of ETH to rETH is completed via open-source contracts.
Rocket Pool Stats
- Total ETH Staked: 427,000 (source)
- Current APR: 5.82% (source)
- Percentage of Total Network: 2.4% (source)
- Unique Node Operators: 2171 (source)
- Staking Commission Percentage: 15% (source)
- Self-Limited: The Rocket Pool DAO has voted in favor of self-limiting
Governance Structure
Rocket Pool distributes staked Ethereum amongst their large network of node operators. The rules of the protocol strongly enforce cooperation from these node operators:“Node operators are required to stake as much ETH as they are assigned. If there is ETH loss due to poor node performance, the operator must first compensate the pool's lost ETH with their original 16 ETH and the loss of RPL…Node operators thus have a large incentive to perform well. Node operators are also incentivized by the protocol to stake as much RPL as insurance as possible, due to additional rewards that are given for providing a bigger safety net should they perform poorly.”
In addition to standard node operators, Rocket Pool also features a group of Oracle DAO (oDAO) node operators that “are responsible for the administrative duties required by the protocol that cannot be achieved by Smart Contracts due to technical limitations.”
Rocket Pool’s token, RPL, is used for staking insurance and is also the governance token that powers their Protocol DAO (pDAO). This DAO can raise governance proposals, spend the pDAO treasury, and potentially change certain protocol settings. You can keep track of community initiatives via their governance forum.
How Payouts Work
The design of Rocket Pool is such that the value of rETH vs ETH will continuously increase over time. The value of rETH is determined by the following ratio:
rETH:ETH ratio = (total rETH supply) / (total ETH staked + total rETH contract balance + total rETH share of priority fees + total rETH share of MEV rewards)
Since Beacon Chain rewards, priority fees, and MEV-Boost rewards will constantly accumulate, this means that rETH's value effectively always increases relative to ETH. The rETH/ETH exchange rate updates approximately every 24 hours based on the Beacon Chain rewards earned by Rocket Pool node operators.
A long-term graph of rETH vs ETH shows the consistent rise in value over time:
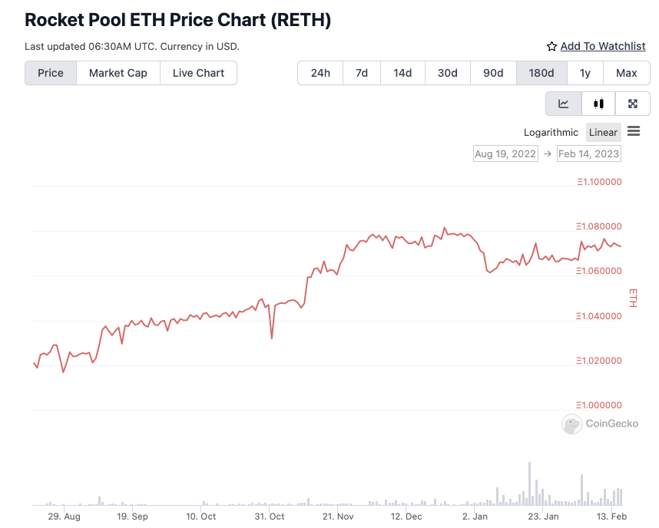
This is helpful for stakers in that it costs no gas to redeem their rewards. The value simply accrues to the rETH token instead.
How to Stake on Rocket Pool
Plans for Withdrawals
Rocket Pool does not currently have plans for a direct mechanism to exchange rETH to ETH once Beacon Chain withdrawals are enabled. Users will still have to primarily utilize the standard swapping mechanism. However, upgrades that influence how individual validators interact with Rocket Pool will be made to coincide with Shanghai.
The most important pending upgrade for Rocket Pool is named Atlas. Currently, Rocket Pool supports full withdrawals of validator stake from the Beacon Chain, but due to the timing of when these contracts were designed, they do not yet support partial withdrawals. Atlas will include support for enabling partial withdrawals, as well as allowing the migration of full existing validators to Rocket Pool, and the conversion of existing 16 ETH minipools to 8 ETH minipools.
Coinbase
URL: https://www.coinbase.com/
Liquid Staking Token: cbETH
Coinbase provides a simple and secure method for existing users of their exchange that stake ETH to receive their liquid staking token, cbETH, in return. They are unique in the world of liquid staking in that they are the only large crypto exchange to also offer a liquid staking product for ETH.
It is important to note that Coinbase does not offer liquid staking for their customers by default. Coinbase users must first opt into staking the ETH that they hold with the exchange. After this opt-in process, they have the opportunity to convert their staked ETH to cbETH.
In the cbETH whitepaper, Coinbase stated that “(W)e we believe that cbETH has the potential to achieve significant adoption and diversify the crypto ecosystem…Keeping Ethereum secure and decentralized is critical to Coinbase’s mission and our hope is that cbETH contributes to that cause…Our hope is that cbETH will achieve robust adoption for trade, transfer, and use in DeFi applications.”
Coinbase Stats
- Total ETH Staked: 2,071,000 (source)
- Current APR: 3.89% (source)
- Percentage of Total Network: 11.7% (source)
- Unique Node Operators: 1
- Staking Commission Percentage: 25% (source)
- Self-Limited: Coinbase has not made any statements regarding self-limiting their staking capacity
Governance Structure
Coinbase does not have any type of web3 native governance structure. They are, however, a publicly traded entity in the United States and subject to the will of shareholders of their COIN stock.
How Payouts Work
Coinbase cbETH is set up similarly to Rocket Pool’s rETH. cbETH is meant to “reflect the price of the underlying staked ETH plus any accrued interest.” You can see this in the graph for cbETH vs ETH which continually increases over time:
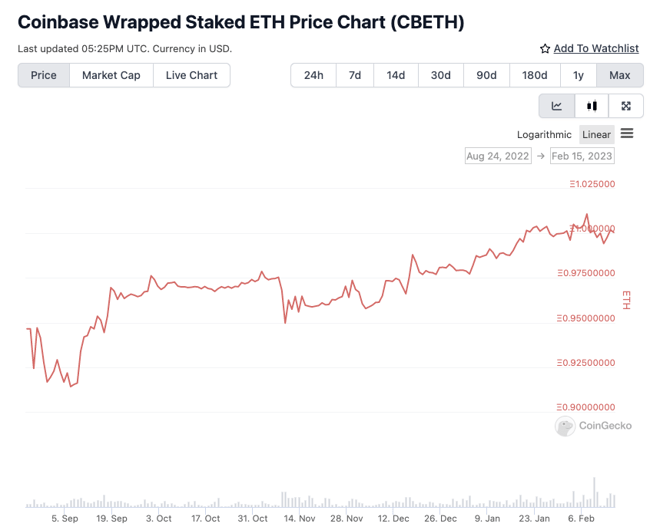
How to Stake on Coinbase
Unlike staking on the other major liquid staking providers listed here, staking on Coinbase requires a Coinbase account. Once you have created a Coinbase account, however, the liquid staking process is fairly similar to other providers.
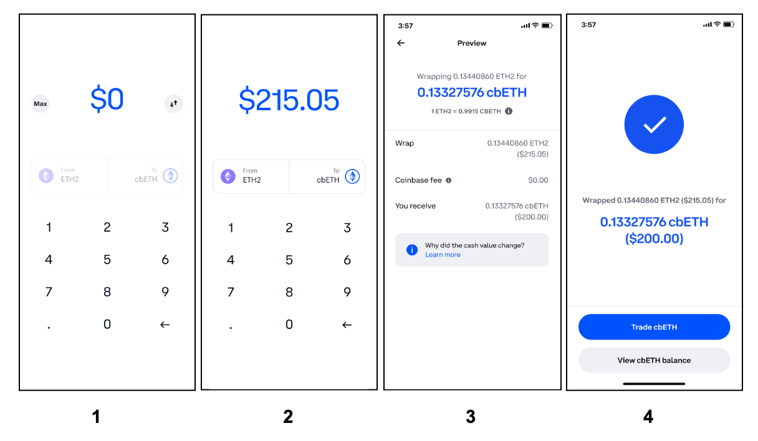
A full walkthrough can be found on this Coinbase support page under the menu item “How do I wrap my staked ETH”. Once ETH has been wrapped into cbETH, users can withdraw from the Coinbase exchange and utilize it as a standard liquid staking token within a web3 wallet while continuing to earn a yield.
Plans for Withdrawals
Because cbETH is designed to steadily increase in value vs ETH, there will be no direct mechanism to exchange cbETH to ETH once Beacon Chain withdrawals are enabled. Users will still have to primarily utilize the standard swapping mechanism. However, thanks to Coinbase’s exchange infrastructure, users can hypothetically expect a more liquid swapping process from cbETH to USD or ETH on the Coinbase site vs what can be guaranteed on strictly web3 native liquidity pools and other liquid staking tokens.
Frax
URL: https://app.frax.finance/frxeth/mint
Liquid Staking Tokens: frxETH & sfrxETH
Frax is a newer player in the liquid staking industry that has gained rapid market share with a unique strategy. While their liquid staking offerings only began in the Fall of 2022, the Frax project itself has been around since 2021 with a suite of stablecoin and DeFi products.
Frax states that “Frax Ether is a liquid ETH staking derivative designed to uniquely leverage the Frax Finance ecosystem to maximize staking yield and smoothen the Ethereum staking process for a simplified, secure, and DeFi-native way to earn interest on ETH.”
Their staking model utilizes a unique two-coin system. This allows them to generally offer a higher APR than most other LST providers. Their contracts are open-source and available for review on GitHub.
Frax Stats
- Total ETH Staked: 105,000 (source)
- Current APR: 6.38% (source)
- Percentage of Total Network: 0.6% (source)
- Unique Node Operators: 1 (source)
- Staking Commission Percentage: 10% (source)
- Self-Limited: Frax has not made any statements regarding self-limiting their staking capacity
Governance Structure
Currently, all validators under the Frax network are operated by the Frax core development team. Plans for a distributed validator system are set to be released to coincide with Ethereum’s Shanghai update and the opening of Beacon Chain withdrawals. Governance of all Frax operations is overseen by holders of the Frax Share token. You can track proposals and community discussions via their governance forum.
How Payouts Work
Frax’s two-coin liquid staking model makes the payout structure slightly different from other protocols. To use Frax, users must first mint frxETH. When ETH is sent to the Frax frxETHMinter, that ETH is added to their liquid staking pool, and an equivalent amount of frxETH is minted. This token does not accrue any staking rewards and is meant to act as an ETH stablecoin. Frax’s stated goal is for frxETH to eventually replace WETH in many parts of the DeFi ecosystem.
Users that hold frxETH only accrue rewards once they, in turn, stake frxETH for sfrxETH. sfrxETH then accrues value vs frxETH thanks to staking rewards. Frax docs explain this process as follows:
“Over time, as validators accrue staking yield, an equivalent amount of frxETH is minted and added to the vault, allowing users to redeem their sfrxETH for a greater amount of frxETH than they deposited. The exchange rate of frxETH per sfrxETH increases over time as staking rewards are added to the vault. By holding sfrxETH you hold a % claim on an increasing amount of the vault's frxETH, splitting staking rewards up among sfrxETH holders proportional to their share of the total sfrxETH.”
The two-coin mechanism of Frax staking is crucial to generating industry-leading yields because not all frxETH is staked for sfrxETH. Frax currently incentives liquidity pools that utilize frxETH so that some users will utilize those pools vs swapping for sfrxETH. This allows the pool of sfrxETH holders to benefit from frxETH deposits without having their rewards share diluted.
How to Stake on Frax
Frax staking walkthrough starts at 4:30:
Plans for Withdrawals
Currently, all users who convert their ETH to frxETH are unable to convert back to ETH directly via the frxETHMinter. However, after withdrawals are enabled on the Beacon Chain, Frax intends to have an unwrap function available to facilitate redemption.
StakeWise
Liquid Staking Tokens: sETH2 & rETH2
StakeWise is, after Lido, the second longest-running liquid staking provider. They launched in the summer of 2021 after half a year of public beta. StakeWise emphasizes resilient infrastructure and expert yield-generation strategies.
Their approach to validators is unique due to cloud infrastructure. According to their docs “when the Beacon Chain applications start to use more RAM or CPU, they are migrated to more powerful servers with zero downtime for the validators” and “whenever more validators and Beacon Chain applications must be launched and current servers do not have enough capacity, the new servers are started”.
StakeWise claims that their cloud infrastructure is capable of creating and maintaining new ETH validators with no human involvement. For each new validator, it automatically finds the server with the most available resources. If a server is not available, it creates a new one. You can review StakeWise’s open-source smart contracts on GitHub.
StakeWise Stats
- Total ETH Staked: 75,500 (source)
- Current APR: 6.39% (source)
- Percentage of Total Network: 0.43% (source)
- Unique Node Operators: 4 (source)
- Staking Commission Percentage: 10% (source)
- Self-Limited: StakeWise has committed to not exceeding 22% of Beacon Chain validators
Governance Structure
The Horcrux manages control of the withdrawal of StakeWise funds. It is a trustlessly generated multisig withdrawal key split into 7 parts with signers that are established members of the Ethereum community. Without these signers, no funds deposited via StakeWise can be withdrawn.
The Stakewise DAO oversees important system parameters such as fees paid by stakers, commissions paid to node operators, the onboarding/offboarding of oracles and node operators, and more. Holders of the SWISE governance token have voting rights in the DAO and governance discussions can be found via the StakeWise forum.
How Payouts Work
StakeWise utilizes a two-coin system for providing payouts to stakers. Users receive the primary staking token sETH2 when they first deposit into StakeWise. Their docs describe the process in this manner: “With every new ETH deposit into the Pool, StakedETHToken contract updates totalSupply and mints an equal amount of sETH2 to the depositor.”
StakeWise’s automated infrastructure handles the validator distribution process: “Deposited ETH first goes to the Pool contract, where it sits with other small deposits until it collects a total of 32 ETH required for a new validator. Once the Pool contract collects 32 ETH, it sends them to the Validator Registration Contract (VRC). VRC registers a new validator entity on the Beacon Chain. Simultaneously, StakeWise Pool adds the new validator to its network.”
Rewards for sETH2 holders are then paid out to them via a separate token, rETH2. Users can track their rewards balance directly via the StakeWise app.
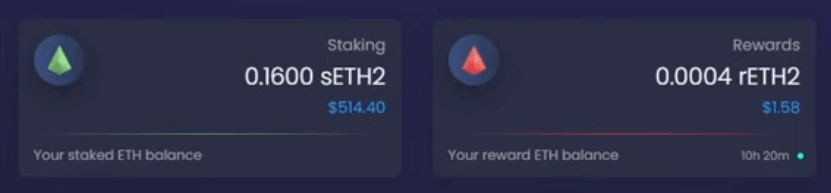
The unique advantage of this approach is that users can restake their rETH2 rewards directly via the StakeWise app. This allows users to compound gains that would otherwise be locked.
How to Stake on StakeWise
Plans for Withdrawals
StakeWise plans to allow users to burn sETH2 and rETH2 within their app and directly receive ETH in return at a 1:1 ratio. The Horcrux will enable this feature by passing control of all pooled funds to a smart contract which will then process withdrawals.
After the Shanghai upgrade, StakeWise is also planning to launch a V3 of the platform. One of the features of V3 is a method for allowing solo stakers to mint liquid staking tokens. This could become a revolutionary feature in that it will provide a path for traditional validators to gain liquidity without withdrawing their funds.
Other Liquid Staking Players
While Lido, Coinbase, Rocket Pool, Frax, and StakeWise make up over 95% of the current ETH liquid staking market, there are other options available for stakers that would prefer to support a minority player:
A few other projects in the liquid staking space that are worth monitoring but are not yet publicly available for deposits include:
Finally, the projects below are not liquid staking providers but are worth monitoring because they plan to support and enhance Ethereum’s future liquid staking ecosystem:
Liquid Staking Options for Node Operators
While most users that interact with liquid staking protocols are individuals that want the convenience of having their staking taken care of for them, there is a smaller group of market participants that is critical to allowing these ecosystems to flourish: validators.
Liquid staking pools automate as much of the validator process as possible, but there are many parts of the validation process that need human intervention. This requires experienced operators that are capable of managing the funds that depositors have entrusted them with.
To attract validators, liquid staking pools generally offer incentives that allow them to earn higher rewards when operating with the pool and managing user funds vs staking on their own. We will outline the different validator incentive programs for the top staking platforms below.
Note: Frax and Coinbase do not offer programs for validators to join their pool. Frax does have plans for a distributed validator system in the future, while Coinbase maintains their validators privately.
Lido
Lido offers information for prospective node operators via their Operator Portal subdomain. According to their documents:“Onboarding rounds are opened on an ad hoc basis as Lido seeks to balance decentralization, node operator profitability, and the overall security of Lido's liquid staking solutions. Currently, the Lido on Ethereum operator set is permissioned (i.e. operators are chosen by the DAO to run validators) given the resiliency requirements and increased risk of managing validators at scale.
The Lido Node Operator Sub Governance group (LNOSG) periodically opens onboarding rounds to balance these aforementioned factors.”
Lido node operators receive their share of protocol rewards as 50% of the 10% cut that is taken from total rewards earned by all ETH staked with Lido. A vote by the DAO can change this fee. The best resource to stay up to date on current Lido node operator news and DAO discussion is the dedicated node operators section of the Lido forum.
Maybe the most important thing for potential Lido node operators to keep an eye on is that the entire landscape of node operation for Lido is set to change with the launch of Lido V2 and what they dub the Staking Router. Lido’s announcement states:
“Thanks to a new modular architectural design, anyone can develop on-ramps for new Node Operators, ranging from solo stakers, to DAOs and Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) clusters. Together, they will create a far more diverse validator ecosystem.”
Lido's Master of Validators, Izzy, has an informative Twitter thread explaining exactly why the Staking Router is so crucial to the future of Lido:
@LidoFinance's proposed Staking Router is an architecture for the allocation of stake across plug and play modules that make pools of validators available for use. Its core ambition is found at the intersection of the simplicity, utility, practicality, and sustainability.
— Izzy (@IsdrsP) February 9, 2023
/1 pic.twitter.com/HXhcTcl71K
Lido's distributed validator technology testing is currently underway with both Obol Network and ssv.network.
This pivot towards modular validator infrastructure could be one of the most important development paths in the history of Lido due to the common critique from some ecosystem actors that Lido has too few unique node operators for the amount of ETH under the protocol’s control. If Lido can successfully open a path towards a more robust and decentralized validator set, it would be a boon for the overall health of Ethereum’s staking ecosystem.
Rocket Pool
Rocket Pool is the gold standard in promoting a decentralized node operator ecosystem with over 50x the number of unique node operators vs the closest competitor (Lido). Rocket Pool primarily incentives node operators to join their collective by lowering the barrier to entry: Rocket Pool requires only 16 ETH to become a node operator vs the traditional 32 ETH. The other 16 ETH that a validator needs to begin operating their full node is provided by rETH stakers. Rocket Pool refers to these 16 ETH validators as “minipools”.
The protocol also differentiates itself from the competition by allowing validators to join and leave permissionlessly. As long as a prospective validator has 16 ETH available, they can follow the instructions available in Rocket Pool’s docs and begin staking. The video below outlines just how easy it is to go from 0 —> validating
If you run into any issues, live support is also available via the Rocket Pool Discord. This level of coverage for prospective validators underscores Rocket Pool’s commitment to being a liquid staking protocol that places just as much importance on onboarding new validators as it does new liquid stakers. While you will need an understanding of command line basics, you’ll have no problem finding the resources you need:
It's very straightforward. The guides are thorough. Familiarity with command line and linux helps, however, most of the set up takes place with a user interface.
— jasperthefriendlyghost.eth | jasper.lens (@Jasper_ETH) February 11, 2023
Plus, the support channel in the discord is constantly active and monitored by dozens of people.
Easier than solo.
Thanks to the outstanding resources available for node operators, Rocket Pool performs the critical community service of filling the gap in offerings between the simplicity of liquid staking and the high-level knowledge that’s necessary for independent solo staking.
The even better news? Rocket Pool is on track to lower the threshold for minipools to 8 ETH. Testing for this capability is underway and set to be released during Q2 2023:
Did you know that running an 8 ETH minipool at @Rocket_Pool is 42.0% more profitable than solo staking?
— dabdab.eth 🦇🔊 (@DabbleWithThis) February 12, 2023
This is even without considering RPL rewards. Pure ETH gains
8 ETH minipools are undergoing audits + testing now and should be out in 1-2 months in the Atlas upgrade
🚀🚀🚀 pic.twitter.com/t9FkLcuSoj
Incentives for Rocket Pool node operators include beacon chain rewards on their staked ETH, commissions on the pooled ETH they manage, and RPL rewards for providing RPL as collateral. At current rates, minipool operators average 7.25% APR on ETH rewards and 10.8% on RPL rewards. They also offer a high degree of control over rewards with their opt-in Smoothing Pool feature that allows operators to choose whether or not they would prefer to be exposed to the randomness of block proposal income.
Liquid Staking vs Solo Staking vs Staking-as-a-Service (SaaS)
For members of the Ethereum community with >32 ETH, the question of whether or not to utilize liquid staking instead of solo staking or using a staking-as-a-service provider can be difficult to answer. While we have already outlined the nuances of liquid staking above, we would also like to present the benefits of choosing not to liquid stake for those who may be weighing their options.
Support Ethereum’s Security & Decentralization
For many users, running an independent validator is important for reasons beyond monetary rewards. The more independent validators there are, the more secure the network becomes. Staking allows individual users to express solidarity with the network’s ethos of community-run technology. It represents a way to directly participate in the governance of web3’s foundation:
Running a solo validator on the Ethereum beacon chain is one of the most empowering expressions of free speech we have. Just one validator. I know it's out of reach for many, but if you're privileged enough to have the opportunity then please take it!
— superphiz.eth 🦇🔊🐼 (@superphiz) August 14, 2022
By increasing the percentage of nodes operated by unique entities, the Ethereum community guards against the potential for a successfully coordinated consensus attack on the network.
Playing the Block Reward Lottery
The dynamic ebbs and flows of economic activity on Ethereum offer a particularly interesting “lottery” aspect for validators who propose blocks. Sometimes, due to a huge demand for transaction space in a limited window of time, priority fees for Ethereum will skyrocket.
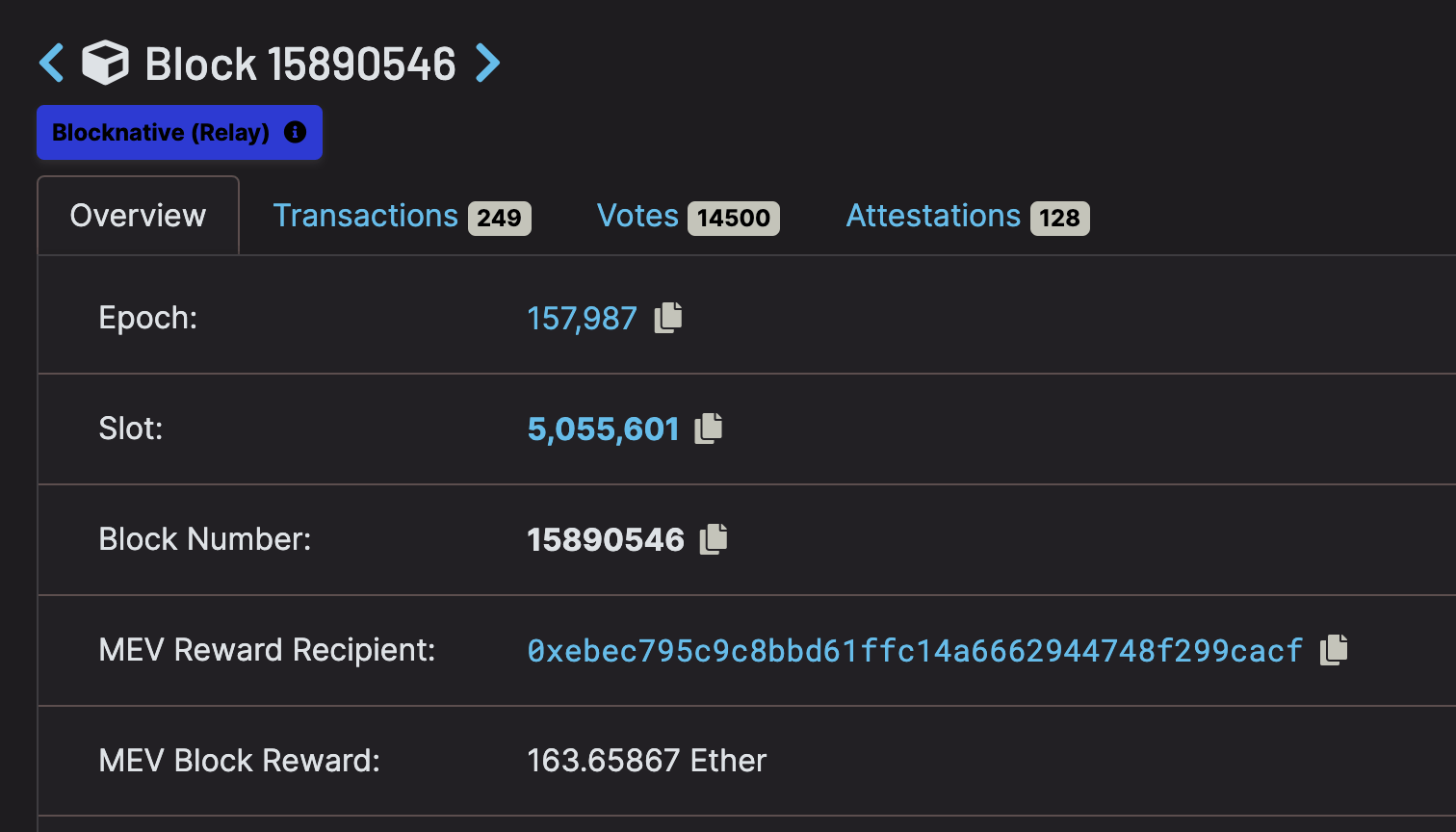
When this happens block rewards can balloon to levels far exceeding the average. A recent example of this comes from the KPR NFT mint. The block below occurred during the timeframe of the mint and netted one lucky validator an astounding 163 ETH value:
When a staker is participating in a liquid staking pool, their rewards are “smoothed” in such a way that the winnings of a lottery block are shared amongst all other pool participants. But if they are operating an individual validator, the winnings of a lottery block like this one would be theirs alone.
The odds are not in favor of individual validators winning these blocks very often, and on average it’s generally more profitable to join a staking pool than to operate a solo validator and play the mempool lottery. But for those who want a chance at huge block rewards, it is best to avoid standard liquid staking pools.
Maintain Complete Control of Your Funds
When you solo stake or use a staking-as-a-service provider, you have complete control over the ETH you have deposited for staking. Solo stakers have direct oversight of their entire operation and SaaS users only provide the service with their signing keys that control Beacon Chain consensus duties. Withdrawal keys are a separate item and they are not necessary for SaaS providers to complete their duties. This means that stakers who utilize a SaaS provider are only at risk for penalties and mismanagement due to incorrect signing. They are not at risk of losing all funds due to the mismanagement of withdrawal keys.
The Future of Liquid Staking
As we saw when reviewing the various upcoming plans for staking services, there is significant energy around protocol upgrades and new services made possible with Ethereum’s Shanghai hard fork and the enablement of Beacon Chain withdrawals. These developments are exciting, but also only represent an initial push into the tech that will be built around the staking ecosystem.
Here at Blocknative, we have often discussed how The Merge’s proto-PBS landscape made it possible for Ethereum block building to become more “modular”. When you break apart the different pieces of block construction, you can decentralize them individually. Doing this allows different actors with certain specialties to focus on their particular strengths. The net result is a more capable network with fewer external dependencies and a lower threshold for participation.
One of Devcon Bogotá’s most interesting presentations centered around Ethereum staking experiencing this same type of evolution. Coinbase protocol specialist Viktor Bunin hosted the talk with guests Stephane Gosselin (prev-Flashbots), Sreeram Kannan of EigenLayer, and Collin Myers of Obol Network.
Ethereum roadmap expert SalomonCrypto has also outlined the possibilities of this “middleware gold rush” in a digestible Twitter thread:
(1/25) @Ethereum Roadmap: Middleware
— Tyrannosaurus Haym (@SalomonCrypto) November 6, 2022
Think back to 2015, does the Ethereum we have today look like what you were imagining back then?
Now think forward to 2030, or even 2122. What will that version of the World Computer look like?
Are you ready for the Middleware Gold Rush? pic.twitter.com/EFqB9Ewh9I
The summary is this: today’s segmented world of individual node operators and large, monolithic liquid staking providers will eventually become a relic of the past. Advancements and adoption of new staking technology will pave the way for the economic value that secures Ethereum to be put to work in securing new applications built on top of the existing tech stack. They will also decentralize how validators operate, lowering the barrier to entry for users that want to participate in securing the network.
Increasing economic activity on Ethereum will also drive this innovation. The Merge occurred at the depths of the 2022 bear market. Because of this, the community has not been able to observe the staking economy during a period of extended peak market demand. If a bull market in Ethereum trading and usage returns, increasing yields from priority fees and MEV will be a powerful dynamic:
2. Staking yield is likely to increase. Despite lower beacon chain rewards the demand for blockspace will continue to create opportunity for MEV.
— Marceau 🏝️ (@marceaueth) January 15, 2023
This is a powerful flywheel that is easy to underestimate and hard to objectively measure. We have yet to see PoS in a bull market.
With all of this in mind, we are experiencing truly exciting times in the world of Ethereum and its ongoing development roadmap.
Boost Your Staking Rewards
Whether you're a solo-staker or you have funds locked in a staking pool, if you're looking to increase your validator's profit it is important that your validator nodes are connected to as many MEV-Boost relays as possible, with as much relay code diversity as possible. This will ensure you maintain highly-available MEV-Boost connections and have exposure to the highest-value blocks available.
If you operate an independent validator, you can add our relay to help promote relay diversity throughout the industry and boost your MEV rewards. If you are an Ethereum holder utilizing a staking service, we recommend reaching out to your provider and encouraging them to connect to a diverse set of relays.
For developers looking to learn more about our relay or help develop it, we recommend reviewing the project on GitHub. If you have questions, you can also join our Discord for live updates and support.
As always, the information provided here is intended for informational purposes only. Nothing in this document is investment, legal, or tax advice. Do your own research. Stay SAFU.
Gas Extension
Blocknative's proven & powerful Gas API is available in a browser extension to help you quickly and accurately price transactions on 20+ chains.
Download the Extension